ISO checklists — written by quality management experts, proven to work, our ISO checklists are available to buy individually or as part of a complete ISO Template. |
ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management System Audit Checklist Page 5 of 49 Clause 4: CONTEXT OF OUR ORGANIZATION 4.1 Understanding our organization and its context Sl. SI.#Au Audit Question Au Audit Result Au Describe the Gap 11 Has our organization determined the external and internal issues that are relevant to its. ISO Checklist Page 1 of 16 Company: Department: Completed by Date completed 4. Context of the organisation 4.1 Understanding the organisation and its context Clause ISO Requirements Reference in your system verification Area of concern? 4.1 Have you determined external and internal issues that are. Internal Quality Management System Audit Checklist (ISO9001:2015) Q# ISO 9001:2015 Clause Audit Question Audit Evidence 4 Context of the Organization 4.1 Understanding the organization and its context 4.1q1 The organization shall determine external and internal issues that are relevant to its purpose. Contact us For more information, read: Risk-based thinking replacing preventive action in ISO 9001:2015 – The benefits and Methodology for ISO 9001 Risk Analysis. Quality Objectives and Plans for Achieving Them The requirements regarding setting the quality objectives remained as they were in the previ. ISO 27001 Checklist questions for Network Security Audit to determine non compliance status and measure the effectiveness of information Security, contains downloadable 3 Excel sheets- 515 Checklist questions covering the requirements of Network Security under Responsibility & accountability of IT department, and Top management of an organization.
| Standard | |||
Internal Audit Checklist The Occupational Health and Safety Assessment Series ISO 18001:2007 audit checklist will help ensure your audits address the necessary requirements. It stands as a reference point before, during and after the audit process. OHSAS 18001 is no longer in date, it has been superseded by ISO 45001 - but this will give you a very good idea of what you will get when you buy an Internal Audit Checklist. | OHSAS 18001:2007 | $0 | free download |
Process Audit Checklist 17 pages, 60 Audit questions.
| ISO 9001:2015 | $0 | free download |
Supplier Audit Checklist 20 pages, 64 Audit questions.
| ISO 9001:2015 | $0 | free download |
Internal Audit Checklist- view sample The audit checklist is just one of the many tools which are available from the auditor’s toolbox that help ensure your audits address the necessary requirements. It stands as a reference point before, during and after the audit process and if developed for a specific audit and used correctly will provide the following benefits:
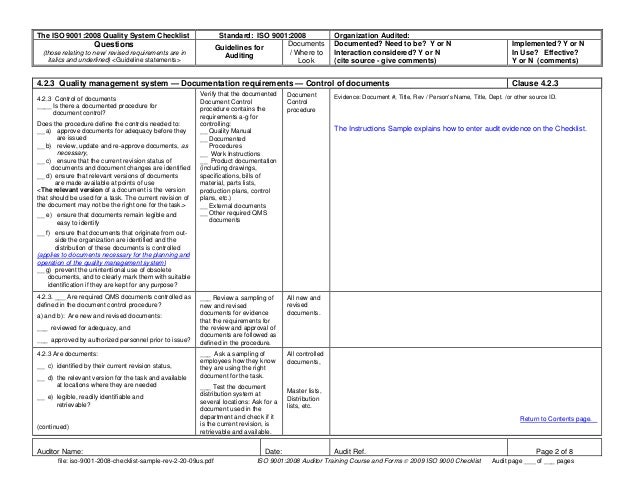
This audit checklist comprises tables of the certifiable (‘shall’) requirements, from Section 4.0 to Section 10.0 of ISO 9001:2015, each required is phrased as a question. This audit checklist may be used for element compliance audits and for process audits. 305 Audit Questions, 78 pages. MS Word. - Context of the Organization | ISO 9001:2015 | $39 USD | add to cart |
Gap Analysis Checklist, Action Plan & Guidance
This gap analysis highlights the requirements contained in ISO 9001:2015. The output provides a valuable baseline for the implementation process as a whole and for measuring progress. It will help you to understand each business process in the context of each of the requirements by comparing different activities and processes with what the standard requires. 50 pages, 158 questions. MS Word.
After completing the Gap Analysis you will have a list of activities and processes that comply and ones that do not comply (GAPs). The latter list now becomes the target of your Action Plan. Next, use the Gap Anaylsis Action Plan to move forward in a proven, structured way.
We find this proven, structured approach is a useful tool to enable stakeholder buy-in and management commitment. The Gap Analysis Guidance explains everything involved as well as detailed instructions for the 5 Steps for completing the gap analysis.
| ISO 9001:2015 | $39 USD | add to cart |
Environmental Internal Audit Checklist - view sample The internal audit checklist stands as a reference point before, during and after the internal audit process. 186 Audit Questions, 41 pages. MS Word. - Context of the Organization | ISO 14001:2015 | $39 USD | add to cart |
Environmental Gap Analysis Checklist - view sample The self-assessment questions will help you to identify gaps between your existing Environmental Management System and the requirements of ISO 14001:2015. 17 pages, 64 Audit questions. MS Word.
| ISO 14001:2015 | $19 USD | add to cart |
Internal Audit Checklist The Occupational Health and Safety Assessment Series ISO 18001:2007 audit checklist will help ensure your audits address the necessary requirements. It stands as a reference point before, during and after the audit process. N.B. This standard has been superseded by ISO 45001:2018 in April 2018. This document is a free download to show you an example Internal Audit Checklist. | OHSAS 18001:2007 | $0 | free download |
OH&S Internal Audit Checklist - view sample Occupational Health & Safety Management System Compliance Auditing The audit checklist will help your audits address the necessary requirements. It stands as a reference point before, during and after the audit process and if developed for a specific audit and used correctly will provide the following benefits:
This audit checklist comprises tables of the certifiable (‘shall’) requirements, from Section 4.0 to Section 10.0 of ISO 45001:2018, each required is phrased as a question. This audit checklist may be used for element compliance audits and for process audits. 264 Audit Questions, 48 pages. MS Word. 4.0 Context of the Organization - view sample | ISO 45001:2018 | $39 USD | add to cart |
OH&S Gap Analysis Checklist and Transition Guide - view sample Although the introduction of ISO 45001:2018 brings a new standard into effect, most of its basic principles are already formulated in OHSAS 18001:2007. A gap analysis of the new requirements is strongly recommended in order to identify realistic resource and time implications. Each clause is addressed showing evidence and action required, along with suggestions and advice upgrading from OHSAS 18001:2007 - view sample The output provides a valuable baseline for the implementation process as a whole and for measuring progress. 18 pages, 40 clauses. MS Word. 4.0 Context of the Organization- view sample | ISO 45001:2018 | $39 USD | add to cart |
3 Internal Audit Checklists bundle (3 separate) ISO 9001:2015 Internal Audit Checklist (as above) - view sample and ISO 14001:2015 Internal Audit Checklist (as above)- view sample and OH&S 45001:2018 Internal Audit Checklist - view sample These internal audit checklists are not integrated or combined, but 3 seperate checklists. | ISO 9001:2015 | $99USD $117 | add to cart |
Integrated Internal Audit Checklist (QMS + EMS) - view sample The checklist ensures each audit concisely compares the requirements of ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 14001:2015, and your EQMS against actual business practice. The audit checklist stands as a reference point before, during and after the internal audit process. 386 Audit Questions, 68 pages. MS Word. - Context of the Organization | ISO 9001:2015, | $69 USD | add to cart |
Integrated Internal Audit Checklist (QMS + OH&S) The checklist ensures each audit concisely compares the requirements of ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 45001:2018, and your QOH&S against actual business practice. The audit checklist stands as a reference point before, during and after the internal audit process. 441 Audit Questions, 26 pages. MS Excel. - Context of the Organization Audit Data Summary (Automated charting) | ISO 9001:2015, ISO 45001:2018 integrated. | $69 USD | add to cart |
Integrated Internal Audit Checklist (EMS + OH&S) The checklist ensures each audit concisely compares the requirements of ISO 14001:2015 and ISO 45001:2018, and your EOH&S against actual business practice. The audit checklist stands as a reference point before, during and after the internal audit process. 301 Audit Questions, 19 pages. MS Excel. - Context of the Organization Audit Data Summary (Automated charting) | ISO 14001:2015, ISO 45001:2018 integrated. | $69 USD | add to cart |
Integrated Internal Audit Checklist (QMS + EMS + OH&S) - view sample The checklist ensures each audit concisely compares the requirements of ISO 9001:2015, ISO 14001:2015 and ISO 45001:2018, and your EHQMS against actual business practice. The audit checklist stands as a reference point before, during and after the internal audit process. 510 Audit Questions. 28 Pages. MS Excel. - Context of the Organization Audit data Summary (automated including graphs), showing: | ISO 9001:2015, | $109 USD | add to cart |
Integrated Internal Audit Template (QMS + EMS) Everything you need to perform an internal audit for ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 together. 3 Checklists, including Internal Audit Checklist - view sample
Plus:
Please note - this is for Internal Auditing. If you are looking for a complete EQMS please click here. | ISO 9001:2015, ISO 14001:2015 integrated. | $299 USD | add to cart |
Integrated Internal Audit Template (QMS + EMS + OH&S) The combined Internal Audit Template contains everything you need to perform an internal audit for ISO 9001, ISO 14001 and ISO 45001 together. 3 Checklists, including Integrated Internal Audit Checklist - view sample
Plus Audit data Summary (including automated graphs), showing:
Please note - this is for Internal Auditing. If you are looking for a complete EHQMS please click here. | ISO 9001:2015, ISO 14001:2015, ISO 45001:2018 integrated. | $399 USD | add to cart |
- Written in International English
- Fully-editable MS Word or Excel files, compatible with Google Docs and Apple Pages
- All the templates use styles – making reformatting and rebranding a breeze
- Immediate download
Pay by Credit Card, Debit Card, PayPal or Apple Pay.
Please read our Money Back Guarantee. |
Successfully Audited and Certified
Used by organizations around the world, our templates have been successfully audited and certified by Registrars & Certification Bodies such as: UKAS, DNV, Lloyds Register, BSI, DNV, BM Trada, LRQA as well as hundreds of independent external auditors.
Used by Thousands of Companies Worldwide
Iso Audit Checklist For Training Department Objectives 2017
Written in International English, bought by small businesses, big brands and individuals our templates have been sold online and CD since 2002.
Used by:
- Small Businesses – dentists, accountants, engineers
- Large Organizations – hospitals, power plants, aircraft manufacturers
The Templates are used by first timers following our step-by-step, clause-by-clause guidance documents; and experienced Quality Managers wishing to streamline and improve their existing documentation.
Five Reasons To Choose Our Templates
- Our customizable templates save you time and money by offering a streamlined process to create your internal audit checklists
- They’ve got everything you need in one simple template
- Our quality manual templates have helped thousands of businesses big and small achieve certification
- Documents use styles to make reformatting and rebranding a breeze
- Our templates are generalizable for any industry or sector. The application of our templates is scalable and generic; regardless of the size and type of organization.
Secure and Trusted
Pay by Credit Card, Debit Card, PayPal or Apple Pay. Our website has been marked safe by popular virus and malware checkers.
More Information
FAQs About Our Templates
Can't Find What You're Looking For?
- Please use the Chat function at the bottom of the screen
- Enquiries [email protected]
- Support [email protected]
- Call 0845 054 2886 (UK)
What is an ISO Internal Audit?
The purpose of an internal audit is to assess the effectiveness of your organization’s quality management system and your organization's overall performance. Your internal audits demonstrate compliance with your ‘planned arrangements’, e.g. the Quality Management System (QMS) and how its' processes are implemented and maintained.
Contents
Don't Try To Manage It All Alone!
Our Internal Audit Procedures & Checklists is proven to work.
Why perform Internal Audits?
Your organization will likely conduct internal audits for one or more of the following reasons:
- Ensuring compliance to the requirements of internal, international and industry standards & regulations, and customer requirements
- To determine the effectiveness of the implemented system in meeting specified objectives (quality, environmental, financial)
- To explore opportunities for improvement
- To meet statutory and regulatory requirements
- To provide feedback to Top Management
| ISO 9001:2015 | ISO 9001:2008 | Summary of Changes | ||
| 9.2 | Internal Audit | 8.2.2 | ISO Internal Audit | This requirement is unchanged from the requirements of ISO 9001:2008 Clause 8.2.2 – Internal Audit. |
Principles of Internal Auditing
Auditing relies on a number of principles whose intent is to make the audit become an effective and reliable tool that supports your company’s management policies and policies whilst providing suitable objective information that your company can act upon to continually improve its performance.
Adherence to the following principles are considered to be a prerequisite for ensuring that the conclusions derived from the audit are accurate, objective and sufficient. It also allows auditors working independently from one another to reach similar conclusions when auditing in similar circumstances.
The following principles relate to auditors.
- Ethical conduct: Trust, integrity, confidentiality and discretion are essential to auditing
- Fair presentation: Audit findings, conclusions and reports reflect truthfully and accurately the audit activities
- Professional care: Auditors must exercise care in accordance with the importance of the task they perform;
- Independence: Auditors must be independent of the activity being audited and be objective
- Evidence-based approach: Evidence must be verifiable and be based on samples of the information available.
Selection of Auditors
Competence level may be measured by training, participation in previous audits and experience in conducting audits. Auditors may be external or internal personnel; however, they should be in a position to be impartial and objective.
When internal personnel are selected to perform an audit, a mechanism needs to be established to ensure objectivity, for instance, a representative from another department may be selected to do the audit.
Audits are demanding and require various forms of expertise. The size of the audit team will vary pending the size of the organization, size and type of operations and the scope of the audit.
Start with Expert Templates, then Make Them Yours
Our Internal Audit Procedures & Checklists is proven to work.
Preparing for the Audit
Before the audit, prepare thoroughly! Spending time in preparation will make you much more effective during the audit - you will become a better auditor. Auditors should not skip this step as it provides much needed value to the audit. Taking the time to prepare and organize actually saves time during the audit.
You should have an up-to-date audit schedule and a well defined audit plan for each process. Be sure to communicate the audit schedule to all parties involved as well as to Top Management as this will help reinforce your mandate.
Gather together all the relevant documented information that relates to the process you will be auditing. Look at process metrics, work instructions, turtle diagrams, process maps and flowcharts, etc. If applicable, collect and review any control plans and failure mode effects analysis work sheets too. Review these thoroughly and highlight the aspects that you plan to audit. Using the documented information in this way ensures they become audit records.
Your organization’s documented information may not cover all of the requirements that may be relevant to the process. If certain information is not available, it may become your first audit finding, not bad for the pre-audit review!

Certain information and linkages should be audited. Some are required and some are simply good audit practice. Putting these sections into a worksheet format gives auditors a guide to follow, to ensure the relevant links are audited.
The Human Aspect of Auditing
Good auditors realize very early on that they are dealing with personalities as much as processes and systems. Whilst the intent of the audit a serious one, often light humor, politeness and diplomacy are the best ways to build rapport. It is vital every effort is made to reassure those being audited that the audit’s primary function is to drive improvement, not to name and shame.
If you are new to auditing, acknowledge this fact, be open and honest. It is also important to explain to the auditees that they are free to express their views during the audit. Remember that you, the auditor, are also there to learn.
Always discuss the issues you have identified with the auditees and always provide guidance on what is expected in terms rectifying any non-conformances or closing out observations you raised. Let the auditees know they are welcome to read your notes and findings; the audit is not a secret.
Try not to be drawn into arguments concerning your observations. It is never appropriate to directly name people in the audit report as this may lead to defensiveness which is ultimately counter productive.
Definition of Internal Auditing
'Internal auditing is an independent, objective assurance and consulting activity designed to add value and improve an organization’s operations. It helps an organization accomplish its objectives by bringing a systematic, disciplined approach to evaluate and improve the effectiveness of risk management, control and governance processes.'
Source: International Professional Practices Framework (IPPF), The Institute of Internal Auditors Research Foundation. Florida, USA, January 2011
Iso Audit Checklist For Training Department Objectives Free
Types of ISO Internal Audit
Internal audits are commonly referred to as ‘first-party audits’ and are conducted by an organization to determine compliance to a set of requirements which might arise from standards like ISO 9001:2015, as well as customer or regulatory requirements.
There are common methods of internal auditing that may be used to determine compliance:
- System Audits
- Process Audits
- Product Audits
System Audits
The system audits are best undertaken using the internal audit checklist. This type of audit focuses on the organization’s quality management system as a whole, and compares the planning activities and broad system requirements to ensure that each clause or requirement has been implemented.
Process Audits
The process audit is an in-depth analysis which verifies that the processes comprising the management system are performing and producing in accordance with desired outcomes. The process audit also identifies any opportunities for improvement and possible corrective actions. Process audits are used to concentrate on any special, vulnerable, new or high-risk processes.
Product Audits
The product audit may be a series of audits, at appropriate stages of design, production and delivery to verify conformity to any specified product requirements, such as dimensions, functionality, packaging and labeling, at a defined frequency.
So, how is an audit conducted?
Use an Internal Audit Checklist
An internal audit checklist will help you to determine the extent to which your organization’s quality management system conforms to the requirements by determining whether those requirements have been effectively implemented and maintained. The
These basic audit questions will help guide the audit in the right direction since the answers they provide often unlock the doors to information the auditor requires in order to accurately assess the particulars of a process.

Consider these common audit questions:
- What are your responsibilities?
- How do you know how to carry them out?
- What kind of training is given to new employees?
- How is the effectiveness of training evaluated?
- Are training records maintained?
- What are the objectives of your processes?
- What is the quality policy and where is it found?
- Which documents do you use and are they correct?
- What outputs does your process create?
- How are your records maintained?
- How do you ensure that products meet the stated requirements?
- Is customer satisfaction data analyzed?
- How do you ensure that products meet the stated requirements?
- What happens when changes are made to product requirements?
- What are the responsibilities/authorities for dealing with non-conformances
- Are there trends in non-conforming products and what's being done about it?
- Is the non-conformance procedure linked to the corrective action process?
- Are employees made aware of the quality policy and objectives?
- Are policies and objectives available and relevant?
- How are quality objectives determined?
- Is there a clear link between the policies and objectives?
- How is progress towards objectives measured and communicated?
- Has the number of customer complaints changed over time?
- What tools are used to identify the causes of complaints?
- How are improvement efforts and successes communicated to employees?
Getting the Most from the Audit Schedule
The audit schedule is divided up to reflect each section of ISO 9001 You should determine which of these sections are of greatest relevance to your business; in other words, which processes, should there be problems, will affect your customers the most. These are the processes that your company must make certain remain stable and consistent. You might wish to schedule these key processes for additional audits, perhaps two or even three times per year.
The audit schedule provides the following benefits:
- Provides a visual plan of the audit programme
- Demonstrates coverage of the whole standard
- Provide current status of the audit programme
- Promotes awareness
Other types of Audit
- Certification Audit (also know as an ISO Compliance Audit)
- Surveillance Audit (this is also an ISO Audit)
Jump Start Your ISO Documentation
Our Internal Audit Procedures & Checklists is proven to work.
Is a Certified Auditor 'Required' To Do An ISO Audit or Can the Company do the ISO Audit Themselves?
You do not need a 'Certified Auditor' to undertake internal quality audits of your management system and its processes.
Certified Auditors normally work for external, third-party accreditation bodies such as DNV, UKAS, LRQA, who will perform the Certification Audit, that is, assess your organization's management system against the requirements of ISO 9001 and provide your certificate of compliance. They will also conduct Surveillance Audits to ensure that your certification is maintained. They would not be involved in day-to-day internal auditing operations.
Internal Auditors can be people from within your organization who posses the necessary competence and impartiality to undertake internal audits in order to ensure effective operation of your organization's processes. The Internal Auditors often report to the Quality Manager.